Strategic Alignment with Business Environment:
Strategic planning, viewed through a systems approach, is the compass that aligns your business with its chosen environment. It involves a comprehensive understanding of your business ecosystem, market dynamics, and internal capabilities. By embracing the principles of systems thinking, strategic planning becomes a dynamic process that ensures your business is agile and resilient.
Adaptability and Scenario Planning:
The systems approach to strategic planning emphasizes adaptability. In a rapidly changing business landscape, the ability to anticipate and respond to different scenarios is paramount. Scenario planning, an integral part of strategic thinking, allows you to envision various futures and proactively shape your strategies to navigate uncertainties.
Cascading Goals and Feedback Loops:
Cascading goals are a key component of strategic planning. Aligning organizational goals with departmental and individual goals ensures a cohesive and coordinated effort. Feedback loops, another principle borrowed from systems thinking, facilitate continuous improvement. Regularly assessing progress and adapting strategies based on feedback contributes to the ongoing success of your business.
Strategic Planning Case Studies:
Explore case studies of businesses that have effectively employed a systems approach to strategic planning. These examples illustrate how aligning goals, fostering adaptability, and incorporating feedback loops contribute to strategic success. Learn from these real-world experiences as you embark on your strategic planning journey.
Interactive Strategic Planning Session:
In our interactive session, we’ll engage in a strategic planning exercise. Identify key elements of your business environment, set cascading goals, and consider potential scenarios. This practical activity will guide you in applying a systems approach to strategic planning, fostering adaptability and long-term success.
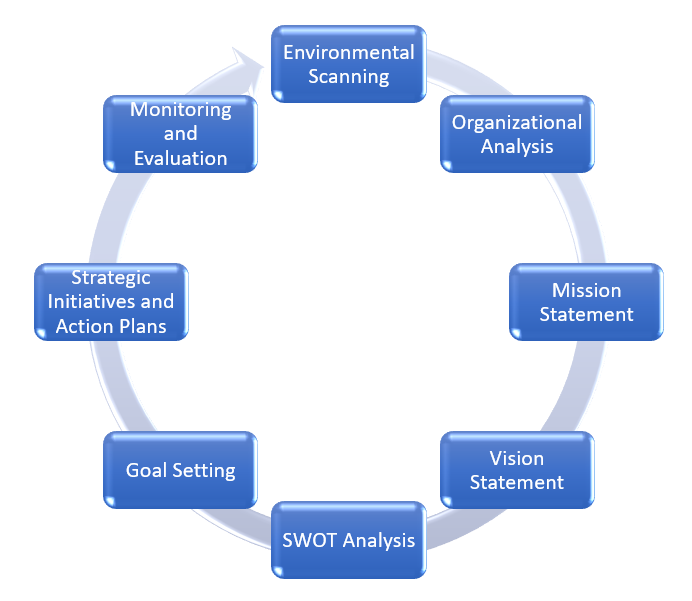
 Strategic planning for small businesses typically involves a series of key steps to ensure a comprehensive and effective approach. There are many different configurations. The main eight steps often include:
Strategic planning for small businesses typically involves a series of key steps to ensure a comprehensive and effective approach. There are many different configurations. The main eight steps often include:
1. Environmental Scanning:
- Assess the external environment to identify opportunities and threats.
- Analyze factors such as market trends, competition, regulatory changes, and economic conditions.
2. Organizational Analysis:
- Evaluate the internal capabilities, strengths, and weaknesses of the business.
- Assess resources, skills, and operational efficiency.
3. Mission Statement:
- Clearly define the purpose and raison d’être of the business.
- Outline the fundamental reason for its existence and the value it aims to provide.
4. Vision Statement:
- Establish a forward-looking vision that articulates where the business aspires to be in the future.
- Inspire and guide stakeholders with a compelling future state.
5. SWOT Analysis:
- Identify and analyze Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
- SWOT analysis helps in formulating strategies by leveraging strengths, addressing weaknesses, exploiting opportunities, and mitigating threats.
6. Goal Setting:
- Develop specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Goals align with the mission and vision and serve as benchmarks for success.
7. Strategic Initiatives and Action Plans:
- Determine the initiatives and projects needed to achieve the established goals.
- Develop detailed action plans with timelines, responsibilities, and resource allocations.
8. Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Establish metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure progress.
- Regularly monitor the implementation of strategies, assess performance, and adapt plans as needed.
These steps provide a structured framework for small businesses to formulate and execute effective strategies. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are essential components to ensure the strategic plan remains responsive to a dynamic business environment.
Transitioning to Business Ecosystem Intelligence
Transitioning from strategic planning to Business Ecosystem Intelligence is a natural evolution in the journey of small business management. While strategic planning focuses on internal and external factors influencing the business, Business Ecosystem Intelligence extends this perspective to encompass the interconnected web of relationships, collaborations, and dynamics within the broader business environment. As we delve into Business Ecosystem Intelligence, the focus shifts from individual strategies to understanding how the business, as a system of subsystems, contributes to and draws from the collective intelligence of its ecosystem. Recognizing the symbiotic relationships between internal systems and the external business community, we navigate the complexities of both structured planning and adaptive responsiveness, fostering a holistic approach to sustainable success.
